10 Quick Ways to Speed Up a Slow PC Running Windows 7, 8, or 10
As your computer ages, it accumulates fragments of temporary files and the hard drive becomes encumbered as a result; after enough time has passed, you will notice a significant difference in your computer's processing speed. While you can't completely negate computer slow-down as it pertains to age, you can do a few things to speed up your computer's processing speed and startup time.
Part: 1
1.
Hold down Ctrl+Alt+Del. This will bring up your PC's task menu. If you have a myriad of programs starting up when you log into your computer, you'll likely have to deal with several minutes of general slow-down. Disabling startup programs will fix this issue.
Click the "Task Manager" option. This will open your computer's Task Manager, from which you can alter or end PC processes.[1]
3.
Click the "Startup" tab. This is near the top of your Task Manager window; doing so will bring up a list of the programs that boot up when you start your PC.
4.
Click on a process you wish to disable. Note that "disabling" a process will not disable it from running at all; rather, it will prevent the program from starting up automatically.
5.
Click the "Disable" button. This is in the bottom right corner of your Task Manager window.
You can also right-click a process and then click "Disable" in the context menu.
6.
Repeat this disabling process for all relevant programs. Some common high memory-usage culprits include Skype and Steam
If you're unsure of which programs to disable, look at the "Startup impact" column on the right side of the Task Manager window; generally speaking, you should disable any "High"- or "Medium"-rated programs.
It is recommended that you leave your antivirus enabled; otherwise your antivirus might not run at startup and thus you would be unprotected from viruses.
7.
Close the Task Manager when you're done. To get the most out of this process, you'll also need to clear out the Hidden Icons menu.
8.
Open the "Hidden Icons" menu. This is the upward-facing arrow on the right side of your taskbar and to the left of your clock. Click or tap it to open your menu.
9.
Review your Hidden Icons menu. Often, you'll find background processes running here (e.g., Dropbox or Google Drive). Killing these processes will free up random access memory (RAM) which will in turn increase your computer's processing speed. You can end these processes from within this menu.
10.
Right-click a process you wish to end. For example, if you aren't using your computer's cloud storage app, you should consider ending this process.
11.
Click "Exit" at the bottom of the context menu. This will usually prompt you to confirm your decision by clicking "Exit (App Name)". You'll need to repeat this process for every single process you want to end.
Part:2. Close System Tray Programs
Many applications tend to run in the system tray, or notification area. These applications often launch at startup and stay running in the background but remain hidden behind the up arrow icon at the bottom-right corner of your screen. Click the up arrow icon near the system tray, right-click any applications you don’t need running in the background, and close them to free up resources.
Part: 3. Disable Startup Programs
Better yet, prevent those applications from launching at startup to save memory and CPU cycles, as well as speed up the login process.On Windows 8, 8.1, and 10, there’s now a startup manager in the Task Manager you can use to manage your startup programs. Right-click the taskbar and select “Task Manager” or press Ctrl+Shift+Escape to launch it. Click over to the Startup tab and disable startup applications you don’t need. Windows will helpfully tell you which applications slow down your startup process the most.
- Part :4. Change your power settingsIf you’re using Windows 10’s Power saver plan, you’re slowing down your PC. That plan reduces your PC’s performance in order to save energy. (Even desktop PCs typically have a Power saver plan.) Changing your power plan from Power saver to High performance or Balanced will give you an instant performance boost.To do it, launch Control Panel, then select Hardware and Sound > Power Options. You’ll typically see two options: Balanced (recommended) and Power saver. (Depending on your make and model, you might see other plans here as well, including some branded by the manufacturer.) To see the High performance setting, click the down arrow by Show additional plans.To change your power setting, simply choose the one you want, then exit Control Panel. High performance gives you the most oomph, but uses the most power; Balanced finds a median between power use and better performance; and Power saver does everything it can to give you as much battery life as possible. Desktop users have no reason to choose Power saver, and even laptop users should consider the Balanced option when unplugged -- and High performance when connected to a power source.
Part : 5. Free Up Disk Space
If your hard drive is almost completely full, your computer may run noticeably slower. You want to leave your computer some room to work on your hard drive. Follow our guide to freeing up space on your Windows PC to free up room. You don’t need any third-party software — just running the Disk Cleanup tool included in Windows can help quite a bit.
Part: 6. Defragment Your Hard Disk
Defragmenting your hard disk actually shouldn’t be necessary on modern versions of Windows. It’ll automatically defragment mechanical hard drives in the background. Solid-state drives don’t really need traditional defragmentation, although modern versions of Windows will “optimize” them — and that’s fine.You shouldn’t worry about defragmentation most of the time. However, if you do have a mechanical hard drive and you’ve just put a lot of files on the drive — for example, copying a huge database or gigabytes of PC game files — those files might be defragmented because Windows hasn’t gotten around to defragmenting them yet. In this situation, you might want to open the disk defragmenter tool and perform a scan to see if you need to run a manual defrag program.
Part: 7.Uninstall Programs You Don’t Use
Open the Control Panel, find the list of installed programs, and uninstall programs you don’t use and don’t need from your PC. This can help speed your PC up, as those programs might include background processes, autostart entries, system services, context menu entries, and other things that can slow down your PC. It’ll also save room on your hard drive and improve system security — for example, you definitely shouldn’t have Java installed if you’re not using it.
Part:8. Turn off search indexing
Windows 10 indexes your hard disk in the background, allowing you – in theory – to search your PC more quickly than if no indexing were being done. But slower PCs that use indexing can see a performance hit, and you can give them a speed boost by turning off indexing. Even if you have an SSD disk, turning off indexing can improve your speed as well, because the constant writing to disk that indexing does can eventually slow down SSDs.
To get the maximum benefit in Windows 10, you need to turn indexing off completely. To do so, first type services.msc in the Start Menu search box, and click the Services result that come up. The Services app then appears. Scroll down to either Indexing Service or Windows Search in the list of services. Double-click it, and from the screen that appears, click Stop. Then reboot. Your searches may be slightly slower, although you may not notice the difference. But you should get an overall performance boost.
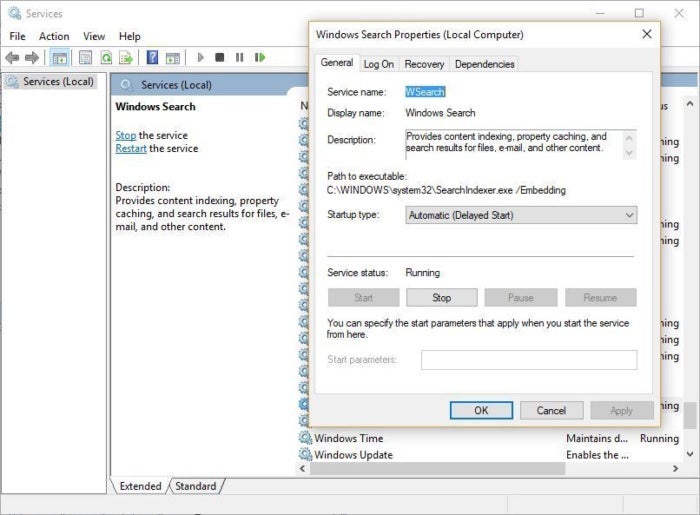
Here’s how to turn off Windows 10 indexing.
If you’d like, you can turn off indexing for only files in certain locations. To do this, first type index in the Start Menu search box, and click the Indexing Options result that appears. The Indexing Options page of Control Panel appears. Click the Modify button and you’ll see a list of locations that are being indexed, such as Microsoft Outlook, your personal files, and so on. Uncheck the boxes next to any location, and it will no longer be indexed.



Emulated storage works to express an actual file path against the symlink of your device’s storage. It can express both the internal memory and the external SD card. A symlink is used in computing to expressed to mean a symbolic link.
ReplyDeleteWhen you go to transfer your files from the pen drive to your Android device or move files from one type of storage to the other, you might see an emulated storage folder is being shown as the main folder.So, what is emulated storage in android?
You might be wondering what it is and why it is shown when it was supposed to show internal storage or external storage card name. Well, in this article, we are going to tell you more about this emulated storage and also what does different kinds of emulated storage mean on Android.